A digital signature acts as a way to send messages through insecure channels without compromising the security of the message or document being sent. Digital signatures do so using encryption. The message from one computer is encrypted in a way that only the receiving computer will be able to decode. In this article, we look at the digital signature process and a digital signature example.
Part 1 Public Key and Private Key in Digital Signature Example
To be effective in ensuring the security of the message, digital signatures have two types of keys: public key and private key.

1. Public Key
The public key is an encryption that is given to the receiving computer by the host computer to enable the other person access to information being sent. But to access the information, the receiving computer must use the Public key from the host computer as well as their own private key.
2. Private Key
A private key on the other hand is vitally different. It is a secret code that allows a computer to encrypt a message before it can be sent over a network. For two computers to gain access to this information or connect on the same network, they must have this private key installed on them. It is essentially a coded language that only the computer with the private key can understand. It is therefore a lot more secure.
Part 2 Example of Digital Signature Process
To get a clear understanding of how the process works, here's a step by step description of just how a digital signature can be sent from one person to another. For the purposes of this description, let's imagine that you are sending a message to a recipient in Office B.
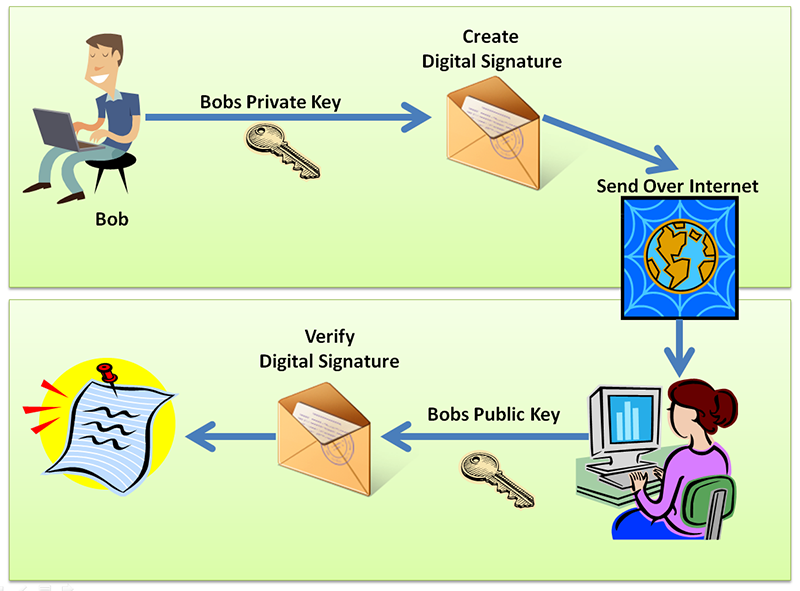
Step 1: You type out a message or create a file with sensitive information. You will then stamp the file with your Private key that can be a password or a code. You press send and the email makes its way through the internet to Office B.
Step 2: When Office B receives the information, they will be required to use your public key to verify your signature and unlock the encrypted information.
Step 3: And then office B needs to use your Private Key (which you have shared with them) to reveal the confidential information on the email. Unless the recipient in Office B has your Private Key, they will be unable to unlock the information in the document.
Part 3 Precautions during Digital Signature Processing
There are several precautions you must take into consideration when processing and using a digital signature as described above. Some of the most prevalent ones, yet easiest to overlook include the following.
- You must ensure that the private key you use (your password) is inaccessible to others. This is both to ensure the security of the information you are sending and the security of your own network and system.
- Share your public key with only those who need the information being sent. And, make sure that the Public key is used only once for the intended purpose. Using the same key for different purposes could compromise the security of information you send in the future.
- Ensure that your private key and public key are different. There is always the temptation to make all your passwords and codes similar in a way. It is convenient but it creates a data security risk.
- In instances where you have to use a digital signature software, ensure that they are compliant with eSignature directives to ensure not just the safety of your signature but also ensure that your signature will be valid and binding. This is especially true for companies that send and receive signed documents to clients.