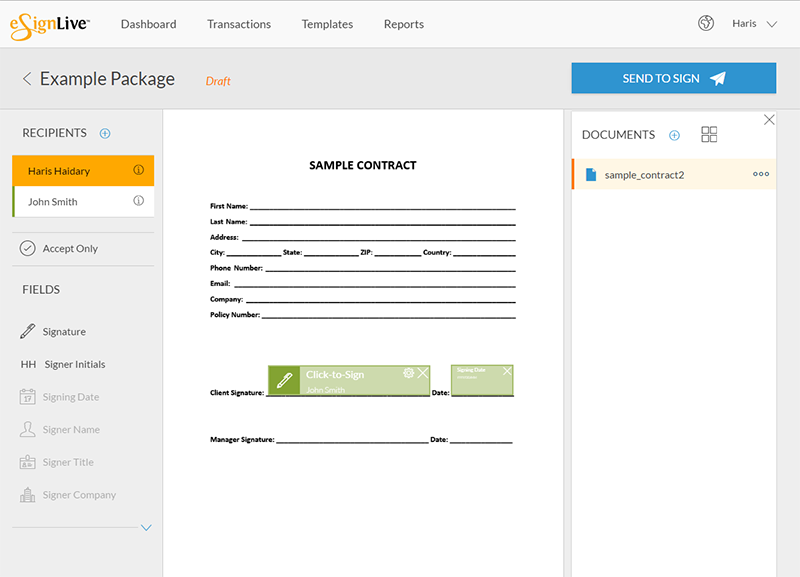
The validity of the digital signature is only assured by the availability and validity of the Public and Private Keys. Both keys are used to encrypt the message in a special digital signature algorithm that further assures security of the message. But what is a digital signature algorithm and how does it work? In this article, we take a closer look at this crucial component of the digital signature process: what it is and how it works.
Part 1 What is Digital Signature Algorithm (DSA)

Introduced in 1991 by the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST), the digital signature algorithm is the standard for digital signatures. Most digital signature types are used by signing messages using the private key of the originator of the message. Because only the message digest is signed, the signature is usually much smaller than the data being signed.
On the other hand, DSA doesn't use the private key to encrypt messages nor does it use the public key to decrypt messages. Instead, DSA makes use of a unique mathematical functions that create a digital signature with two 160-bit numbers. These numbers are originated from the message digests and the private key. While DSA does use the public key to authenticate the signature, the process of verification and authentication is often lengthier and complicated as compared to other types of digital signatures.
Part 2 What is Digital Signature Standard (DSS)

The digital signature standard (DSS) is a type of digital signature algorithm that was developed by the U.S. National Security Agency (NSA) to generate digital signatures for the authentication of electronic systems. This digital signature algorithm, put forth by the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) in 1994 has become the standard algorithm for the authentication of electronic documents. It is specified in the Federal Information Processing Standard (FIPS).
DSA is a pair of large numbers. The numbers are generated within a specified algorithm that enables the authentication of the signatory. The signatures are generated with the use of the private key and verification uses the public key. Each signatory will have their own public and private key. A signature can however only be generated by an authorized person using their private key and the corresponding public key can then be used by anyone to verify the signature.
A message digest (also known as a summary of the information) is created by using a hash function (the Secure Hash Standard). This summary is conjunction with the DSA algorithm is used to create a digital signature that is sent with the messages. The verification process also uses the same hash function.
So, while the DSA is the more commonly used digital signature algorithm, both the DSA and the DSS ensure the security of the message by encrypting the message in a way that only the singing and verifying entities can be privy to it. The mathematical algorithms used in each case ensure the validity of the signature and the message.